Alkenes
the family of alkenes are said to be unsaturated hydrocarbons.
The Alkene Names, And Its General Formula.
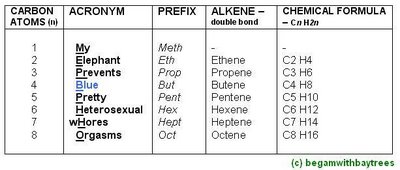
*no methene available
Preparation
alkene molecules can be prepared by cracking alkanes.
hydrogen is formed as a result of the cracking process.
alternatively, medium-sized alkanes undergo cracking
to form smaller, more useful
alkanes (octane for petrol)
and alkenes (ethene)
which can be used to form plastics like polyethene.
(for a diagram, refer to page 272 of our comprehensive chemistry text book.)
Combustion
alkene + oxygen -> water + carbon dioxide
Addition Reaction
*characteristic reaction of unsaturated compounds
*addition reaction is fater than substitution reactions
hydrogenation:
alkene + hydrogen -> alkane
bromination:
bromine decolourises from brown to colourless when reacted with alkenes.
hence the bromine test is used to distingush alkenes from alkanes.
hydration:
alkene + water -> alcohol
polymerisation:
alkenes can join together to form giant molecules called polymers.
*polymer = thousands of identical units called monomers joined together.
eg. the polymer - polyethene, is made up of many ethene monomer molecules.
(this will be further explained in the unit macromolecules. yuck. =P)
in short,
-the general formula for alkenes is Cn H2n.
-alkenes are often formed by cracking alkanes.
-combustion products are CO2 and water.
-alkenes undergo addtion reactions as they are unsaturated molecules because they contain double carbon-carbon covalent bonds.
-alkenes can undergo polymerisation.
chill-
0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home